Program delays challenge management in all types of enterprise – profit, non-profit, public and private. Stalls, stumbles, delays and barriers seem to randomly and inconveniently attach themselves to all types of organizational initiatives. Whether a firm is struggling with a critical initiative intended to dig its way out of a stuttering economy or dealing with the challenge of quickly responding to unprecedented growth in customer demand for its new product, all initiatives hit roadblocks.

Some suggest that roadblocks are simply a way of life in business – inevitable. That may be true. But if these banes are inevitable and ubiquitous, shouldn’t the management tool kit and training programs of the firm include an effective method for dealing with them?
I am not going to tell you that I have discovered some magic formula for the total avoidance of stalls, stumbles, delays and barriers. Rather, I will share a process and 12-point checklist for rapidly discovering their root cause and overcoming them.
From a Fiddler, comes insight
My insight into this common challenge came from the following scene in the movie Fiddler on the Roof.
Tevia, a poor Jewish farmer in Czarist Russia, is attempting to deliver fresh milk to the townspeople from his farm on the outskirts of town in time for the Sabbath. Tevia is pulling a heavy, wooden two-wheeled cart ladened with cans of milk, the harness around his own neck because his horse has come up lame. He is determined to fulfill his obligation to deliver – leaning forward and pulling in the summer heat on a dusty, gravel-strewn road.
I pondered Tevia’s circumstances. Should a pebble in the road find its way into the path of one of the cart wheels, progress would immediately come to a halt. Tevia would be faced with a choice – either attempt to lift a 400-pound cart over the pebble, or, simply remove a pebble.
The business insight?
Discovering and removing pebbles is the true challenge in making progress on a stalled business initiative ~ not pushing harder or lifting.
A process for discovering and removing pebbles:
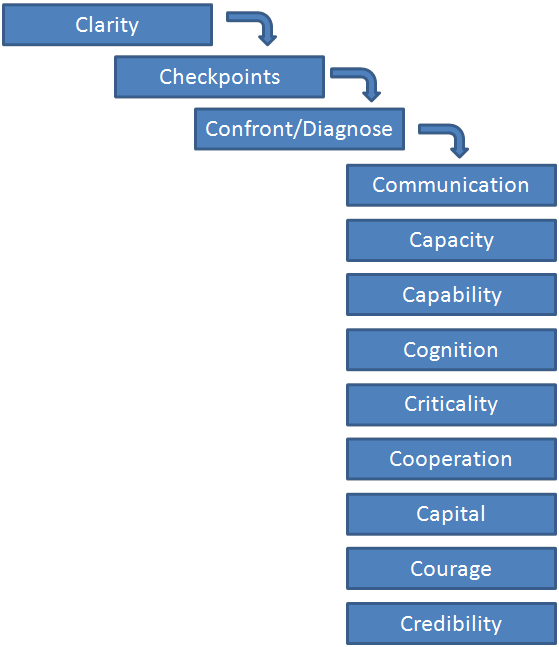
The process we offer has four parts: 1) the nurturing of a Culture of Immediacy and sense of urgency around identifying, diagnosing and fixing delays 2) the discipline of having frequent Checkpoints, 3) immediate Confrontation of the stall and 4) a Checklist of 9 C’s for quickly diagnosing and overcoming the real barriers to progress.
All steps begin with the letter “C”.
Culture: An organization’s culture usually reflects the CEO’s vision and personal example. A disciplined drive to get things done, supported by a culture of immediacy and a sense of urgency will keep the momentum going.
Checkpoints: Frequent Checkpoints is the second most important “C”. Checkpoints are not micro-management. The purpose of a checkpoint is to discover and address barriers and enable progress – not target and fix blame. Barriers and pebbles are discovered quickly and time loss is minimal with frequent Checkpoints.
To punctuate the point, we recommend clients change the company vocabulary by striking the words “Meeting” and “Review” from all company communication and replacing them with the words “Working Session” and “Checkpoint” respectively. These new words imply a strong need for, and set the uncompromising expectation of, the active participation of all members of the team to drive to make progress. These changes in lexicon create a new cultural baseline if this drive didn’t exist prior to the vocabulary change and reinforces it if it did. Participation replaces passivity. Passively sitting back and watching someone present becomes forbidden.
Managers and leadership must demonstrate hands-on participation in these working sessions. They must lead problem solving, knock down barriers and be decisive. Working sessions should end with the following questions: Who is specifically going to do what, by when, to remove the discovered pebbles? Does anyone see any additional barriers or pebbles immediately ahead of us in the road? When is our next checkpoint?
Confrontation: Confrontation does not mean argument. It suggests immediacy, persistence and determination in overcoming a barrier. It means seeing a discussion through until a solution or path-to-a-solution is agreed upon – and not giving up until it is.
People are not confronted in working sessions – barriers are. A combination of objective tough-mindedness and social courage is required to confront a delay discovered during a working session.
In 20 years of consulting, I have found the lack of these two C’s (Checkpoints and Confrontation) are extremely common at all management levels. If the CEO or leader demonstrates a lack of discipline for checkpoints and a reluctance or fear of confronting barriers, the organization will reflect that “looseness” of good management discipline and process.
The 9 C’s Checklist
The list below identifies the most common root-causes of delays in business initiatives. Once you have identified the correct root cause “C”, you can jump to the only “C” that is not on the list – Correct It.
Communication: The importance of this first “C” cannot be over-emphasized. Communication-related delays occur because someone has overlooked the need to communicate something that needed to get done, when it needed to be done and why. It’s difficult to communicate too much.
Capacity: Insufficient personal or organizational time available to complete important tasks can cause delays. Most of the time critical task delays that are laid on the doorstep of Capacity are really related to inappropriate or misaligned priorities.
Capability: Occasionally a team member’s lack of understanding of how to tackle the task at hand creates a delay. In such a case, outside expertise or training will break through the barrier. This is a particularly nefarious “C” because individuals rarely want to admit that they simply don’t have the skills or knowledge to get around the problem – which brings us to the next “C” – Courage.
Courage: Progress often requires personal behavioral change. We all know how difficult it is to accomplish behavioral change – personally and organizationally. Personal courage comes into play most often, when an individual does not have Capability but is afraid to admit it.
A second type of Courage is organizational. We have a good historical example from the 1980’s – the adoption of Total Quality Management disciplines by most major manufacturing firms in the country. This change represented a major shift and courageous commitment made by executives. One of its primary tenets was to first “drive out employee fear”. Honest, open communications, generated from data and fact, and rewarding people who identified and overcame barriers earlier rather than later, helped drive out the fear of enable the desperately needed change.
Co-operation: Typically, what appears as a delay caused by a lack of cooperation, either from an individual on the project team or from a support department, is actually caused by a priority misalignment. Management Clarification and Communication quickly overcome these barriers.
Cognition: Ever been caught in a “deplaning jam”? It’s the experience of de-boarding quickly from an airplane only to be jammed-up in the terminal by Grandma hugging all her six grandchildren right in front of you? People scurrying on their way to catch a cab or to baggage claim start crashing into one another as they stop short – preferring that collision to crushing Grandma and the youngest granddaughter wrapped around her leg. Grandma has stopped and stalled progress – oblivious to the consequences of her behavior.
Sometimes people simply don’t know they are in the way of progress by their inaction or that what they are doing is counter-productive.
Criticality: The negative economic implications of delays (and the positive economic implications of rapid success) should be visible to all members of a project team. Creating and sustaining a sense of urgency is essential by the manager ultimately responsible for the P&L impact of the program. When a delay is on the critical path it must be confronted immediately. Again, sometimes people just don’t realize the critical nature of a task assigned to them. Setting deadlines helps punctuate criticality.
Credibility: Do the team members really believe there is a need for the change initiative? Do they trust the judgment of the management team? Has the management team’s judgment proven itself in the past, demonstrated by a good track-record of success?
Trust doesn’t happen overnight and a lack of trust may linger just beneath the surface, as a pebble that is difficult to see – perhaps buried in a small puddle of passivity. In such a puddle, you can’t see the pebble, but you can feel, see and hear its effect. You may be afflicted by a Credibility pebble if you hear the phrase, “Program du jour”, notice a roll-of-the-eyes in the ranks of the team when the objectives are described, or recognize a blasé attitude..
Capital: Sometimes funding is needed to overcome a barrier. In some cases there is an ingrained philosophy, or unspoken rule of not asking for funding. To overcome this hesitancy, set expectations at the beginning of an initiative to make capital-related issues visible immediately.
Example: A Persistent Barrier Falls to 3 of the “C” Questions
A number of years ago I was working with a client to rebuild their weak sales pipeline. When I asked the sales manager what he thought the barriers were, he answered, “Time”. In our vocabulary that “C” is Capacity. He continued, “We have to baby-sit every project opportunity from birth to death – including project coordination. This makes us too busy to look for new business.” I suggested that they document the customer engagement process, divide it into phases and assign different phases to different departments– freeing up their time to engage more new customers and new projects. Stunned silence was the response. No one had thought to solve the bottleneck by looking at it as a process capacity issue instead of a sales problem
I asked, “Is there anything else in the way? He said, “Training. We don’t know how to use the pipeline management system.” In our vocabulary that “C” is Capability. We scheduled training for the next sales meeting.
“Anything else”, I asked? He said, “The CRM system isn’t designed for our business”. They ordered a new, easy-to-deploy system that fit the business better. It could be installed in the next 45 days in time for the next sales meeting and would cost only a few thousand dollars. That “C” is Capital.
Anything else? “Nope”
I then suggested a series of working sessions, (Checkpoints), over the ensuing several weeks to assess progress on these pebbles and identify any new or additional barriers.
These pebbles had been jamming their cart wheel for more than two years. In one hour, using our list of “Cs” we identified and began the process of removing them. You can too – if you have the Commitment and the Courage to Confront them.
*****
Learn more about a QMP program for deploying a culture of Performance Excellence and Getting Things Done
![]()